Warning
You are reading an old version of this documentation. If you want up-to-date information, please have a look at 2025.11 .Backlights
Colors option
Following backlights are available:
Color |
Wavelength 50/80 |
Wavelength 240/380/530 |
|---|---|---|
Blue |
465 nm |
465 nm |
Green |
520 nm |
550 nm |
Infrared |
880 nm |
850 nm |
Red |
640 nm |
645 nm |
White |
6500 K |
6500 K |
If this option is ordered at the same time with the Asycube, it is delivered mounted in the feeder
Note
For more information on the backlight color and the procedure to exchange the backlight, please refer to Exchanging / Installing the backlight
Note
For more information on the backlight danger please refer to Danger
Select backlight color
For most of the application, the color of the lighting does not matter, especially for opaque parts. For this reason, we advise the standard red color.
It may be difficult to see translucent parts if their color is close to the color of the backlight. The part may merge a bit with the background. This may be the case even with plastic parts that looks opaque to the eye.
In the example below, when illuminated with a red backlight, the contrast between the yellow clips and the background is compromised (even if the clips look opaque with ambient light).
When illuminated with a blue backlight, the same part will have a much higher contrast against the background. This is because the blue color is the complementary color of the yellow and is therefore better absorbed than the red one.
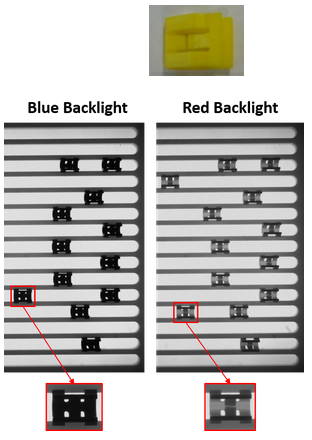
This is because the yellow color is closer to the red than to the blue in the chromatic circle.
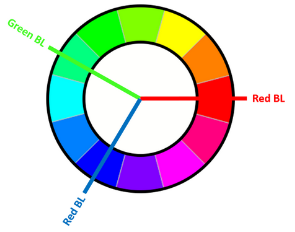
To maximize the contrast, the color of the backlight should be at the opposite of the color of the part.